

This page is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Melissa Alviar-Agnew, Henry Agnew, and Lance S. The atomic mass unit (amu) is a unit of mass equal to one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom.As a result, a neutral atom must have an equal number of protons and electrons. The positive charge on a proton is equal in magnitude to the negative charge on an electron.
Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, but they are both much more massive than electrons (approximately 2,000 times as massive as an electron).Also, shells don't stack neatly one on top of another, so don't always assume an element's valence is determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. An atom can acquire a positive charge or a negative. Remember that an element's electron cloud will become more stable by filling, emptying, or half-filling the shell. Like protons, neutrons are bound into the atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. It is charged because the number of electrons do not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they are neutral).Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force.

Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge.Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge.The barium cation is written Ba 2+, not Ba +2.\): Properties of Subatomic Particles Particle Note the convention of first writing the number and then the sign on a multiply charged ion.
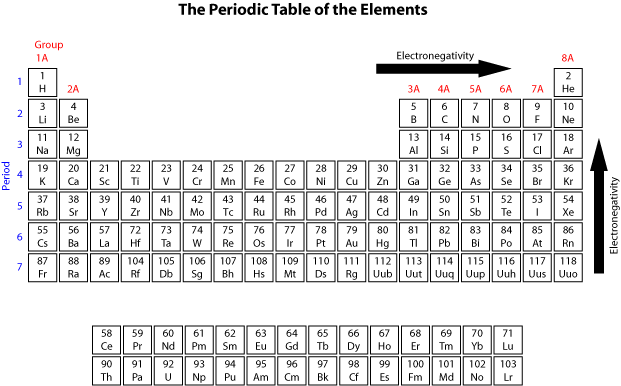
Figure 3.3 "Predicting Ionic Charges" shows how the charge on many ions can be predicted by the location of an element on the periodic table. On the other side of the periodic table, the next-to-last column, the halogens, form ions having a 1− charge. Ions made from alkaline earth metals, the second group on the periodic table, have a 2+ charge. For example, all ions made from alkali metals, the first column on the periodic table, have a 1+ charge. Thus, the periodic table becomes a tool for remembering the charges on many ions. In many cases, elements that belong to the same group (vertical column) on the periodic table form ions with the same charge because they have the same number of valence electrons. In macroscopic samples of sodium chloride, there are billions and billions of sodium and chloride ions, although there is always the same number of cations and anions. Atoms are electrically neutral because the number of protons, which carry a 1+ charge, in the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of electrons, which carry a 1- charge, in the atom. Image credit: Wikipedia Commons, public domain. The number of electrons lost by the sodium atom (one) equals the number of electrons gained by the chlorine atom (one), so the compound is electrically neutral. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound made up of sodium ions and chloride ions in a crystal lattice. Notice that there are no leftover electrons. The resulting combination is the compound sodium chloride. With two oppositely charged ions, there is an electrostatic attraction between them because opposite charges attract. On the right, the chloride ion has 18 electrons and has a 1− charge. On the left, the chlorine atom has 17 electrons. Most nonmetals become anions when they make ionic compounds.įigure 3.2 The Formation of a Chlorine Ion Negatively charged ions are called anions A negatively charged ion. The two positive charges on the two sodium cations balance out the two negative charges on the oxide anion. When these atoms gain electrons, they acquire a negative charge because they now possess more electrons than protons. Some atoms have nearly eight electrons in their valence shell and can gain additional valence electrons until they have an octet. Most metals become cations when they make ionic compounds. Positively charged ions are called cations A positively charged ion. Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result because they are left with fewer negatively charged electrons to balance the positive charges of the protons in the nucleus. In cases where an atom has three or fewer valence electrons, the atom may lose those valence electrons quite easily until what remains is a lower shell that contains an octet. Some atoms have only a few electrons in their outer shell, while some atoms lack only one or two electrons to have an octet. Most atoms do not have eight electrons in their valence electron shell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
